- dr.ishan.shevate.pune@gmail.com
- Baner, Pune, Maharashtra 411045
- Mon - Sun: 9:00 am - 9:00 pm
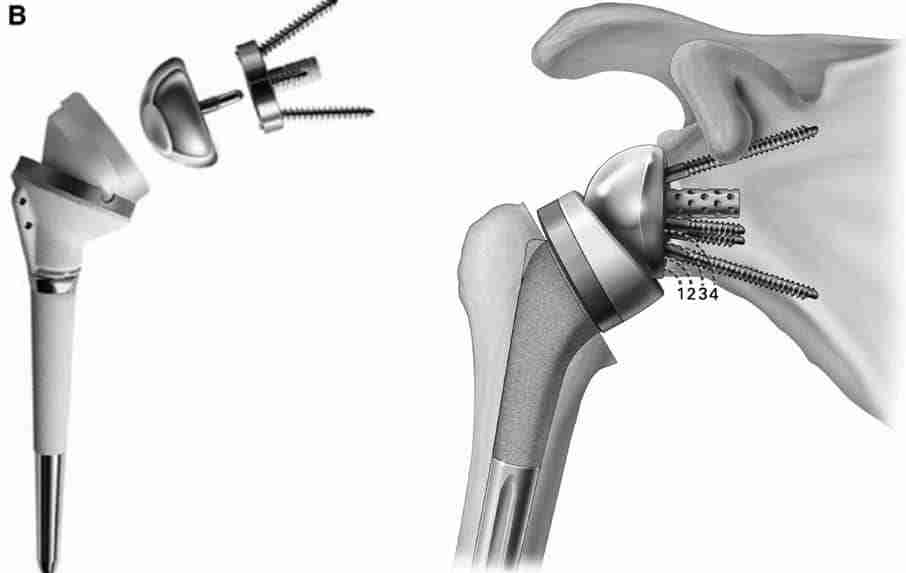
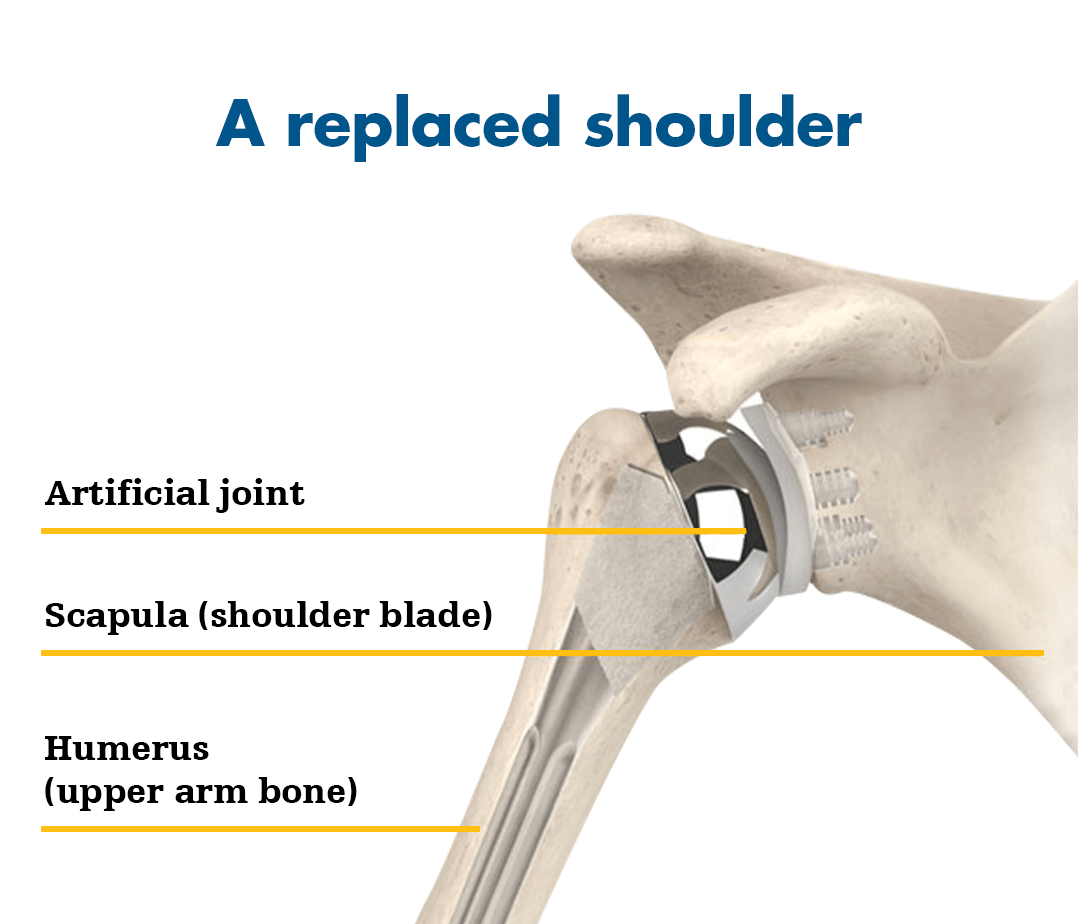
Dr. Ishan Shevate is a highly regarded orthopedic doctor and expert shoulder surgeon based in Baner, Pune.
Visiting Hours
| Mon - Fri: | 8:00 am - 8:00 pm |
| Saturday: | 9:00 am - 6:00 pm |
| Sunday: | 9:00 am - 6:00 pm |
Gallery Posts